Discover the wonders of the human body, from anatomy and development to sexual identity.
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are infections (bacteria🧫, virus🦠 or parasites that grow in or on the body) passed primarily by sexual contact with an infected person. They are usually spread by having vaginal, oral, or anal sex. They are also called sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and are among the most common health illnesses that affect adolescents in Nigeria.
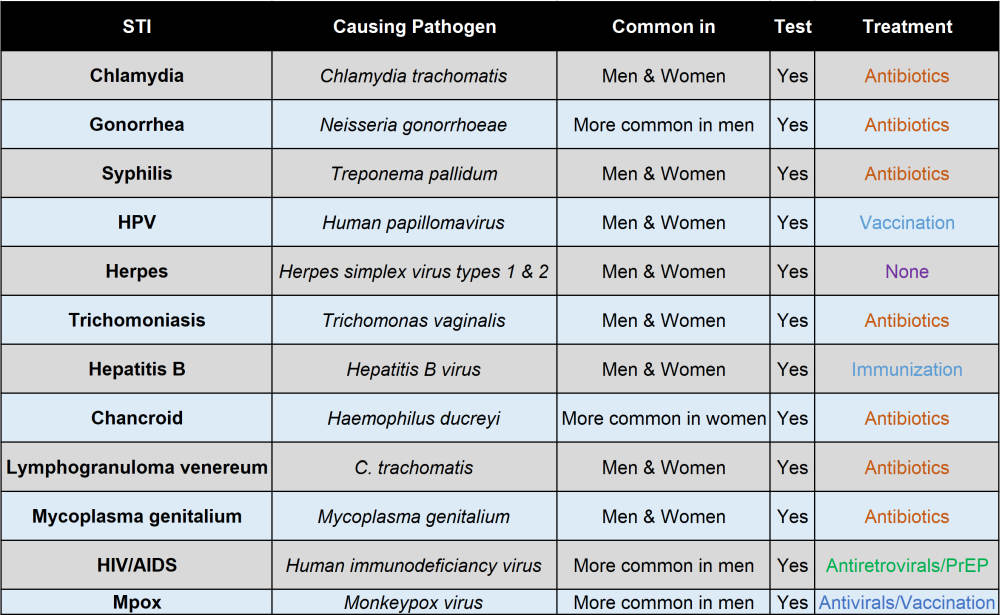
Types of STIs include gonorrhoea, syphilis, genital herpes, chlamydia, trichomonas, hepatitis B etc
Females are at more risk of getting infected with STIs than males because their vagina gets infected more easily and they are also less likely to know they are infected because they have fewer signs/symptoms which are easily noticed. When STIs are not treated, it can lead to serious, long-term health problems. Going for regular tests if you are sexually active is therefore important. Some of the signs and symptoms are:
Some of the health complications of STIs include:
Many young people engage in risky sexual practices that increases their risk of getting STI as well as other negative, immediate and long term consequences such as
How to test for HIV
Usually, individuals with HIV infection usually have no symptoms and may not know until they get tested. Blood or saliva tests can be done to know your HIV status. It takes about three months before the test can show if an individual has HIV after they get infected, this period is called the window period. It is important to note that the virus can be passed to other people during the window period. While you can buy a self test kit for a blood test, it is also now possible to buy an oral test kit which allows one to test for HIV anywhere and get the result in a short while. The test kit is affordable. The benefit lies in the ease of the test. No blood and full confidentiality. Remember however that even if the test result is positive, you need to see a professional in a healthcare facility. There are persons living with HIV today who have been living with the virus for over 20 years and some even more.
People living with HIV/AIDS🧬 with the right care, treatment and support are also able to live productive lives and to have children of their own if they wish to. Therefore, they should not be discriminated against or stigmatised. They have the right to equal love, care, respect and support just as everyone.
Prevention of STIs
STIs can be prevented through the following:
Treatment of STIs
Prevention, they say, is always better than cure. Some STIs are curable i.e. the germ causing the STI is completely removed from the body e.g. syphilis, gonorrhoea, penial wart, chlamydia and trichomoniasis while some STIs cannot be cured but can be treated or managed e.g. herpes simplex virus (herpes), hepatitis B, and HIV. Persons who have HIV can receive antiretroviral (ARV) drugs💊 which keep the virus at low levels and enable such persons to live normal productive lives.
Individuals who have any signs or symptoms of STIs must:
We use cookies to improve your experience on our site. By using our site, you consent to cookies.
Manage your cookie preferences below:
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
These cookies are needed for adding comments on this website.
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us understand how visitors use our website.
Google Analytics is a powerful tool that tracks and analyzes website traffic for informed marketing decisions.
Service URL: policies.google.com (opens in a new window)